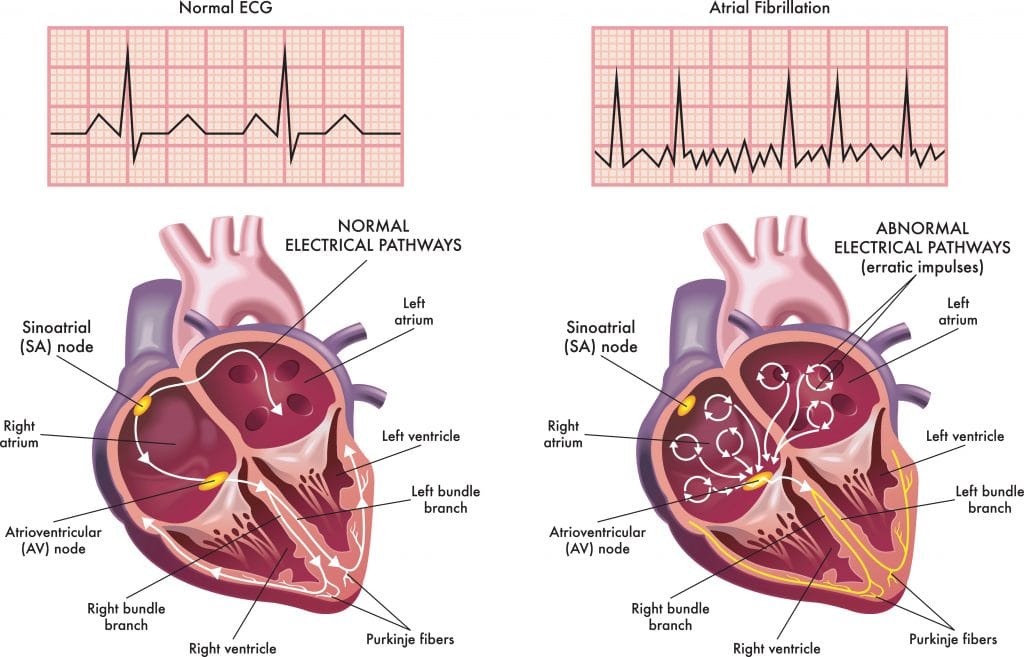
What Is Atrial Fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation is a common heart rhythm disorder in which the heart’s upper chambers (atria) beat irregularly or too quickly, causing the heart to work less efficiently. This can increase your risk of stroke, heart failure, and other complications. Some people notice palpitations, fatigue, or breathlessness, while others have no symptoms—especially women, who may experience more subtle warning signs. Early diagnosis is crucial, as afib can be “silent” until a complication arises[^1].
Why Addressing Afib Matters
Afib affects nearly six million Americans, with numbers rising as the population ages and conditions like obesity, diabetes, and sleep disorders become more common[^1]. Heart disease remains the leading cause of death in the U.S., and women are especially likely to experience less obvious symptoms—such as unexplained fatigue or mild chest discomfort[^1]. Recognizing these signs and seeking timely treatment can help reduce the risk of serious outcomes like stroke or heart failure.
Benefits of Treating Atrial Fibrillation
Treating atrial fibrillation can restore a more normal heart rhythm, reducing symptoms and improving your energy and ability to stay active. Most importantly, treatment significantly lowers your risk of stroke by helping prevent blood clots. Treatment options—including medications, procedures, or devices—can also decrease the likelihood of long-term heart damage. In some cases, non-medication approaches may reduce the side effects linked with long-term use of blood thinners, such as bleeding or digestive issues.
Comparing Afib Treatments and Costs
Initial treatment often involves medication, but if medications are not effective or cause side effects, other options are available. Catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that targets the malfunctioning areas in the heart. While costs vary, the out-of-pocket expense for catheter ablation with insurance may range from $5,000 to $10,000, depending on your specific plan[^2]. For those unable to take blood thinners, the Watchman device—a small implant that reduces stroke risk—may be considered. Patients and doctors often compare the Watchman device vs. blood thinners like Eliquis for safety, lifestyle impact, and cost. Each treatment has benefits and risks: ablation and devices can lessen the need for daily medication but have their own potential complications, such as bleeding or rare heart damage[^3]. Medication side effects, including bruising and drug interactions, are also important to discuss with your provider.
Choosing the Right Afib Treatment Plan
Discuss all available options with your cardiologist to create a plan that fits your health profile and lifestyle. Key questions to consider:
– Am I a good candidate for ablation, or should I continue with medication?
– Do I have increased bleeding risks or other health considerations?
– Am I able to manage daily medication routines or monitor blood levels if needed?
– What are the expected outcomes and recurrence rates for ablation in my case? (Success rates can range from 60–80% after one year[^4].)
Some individuals explore natural approaches, like diet or supplements, but these should never replace prescribed treatment unless directed by a physician[^5]. Always consult your healthcare team before making any changes to prescribed therapy.
Potential Challenges and Risks to Avoid
Every afib treatment option has its limitations. Catheter ablation is not always a permanent solution—recurrence rates vary based on age, heart health, and type of afib. Medications may cause side effects such as fatigue, bleeding, or dizziness. If your current treatment is not working, your doctor may recommend medication adjustments, a repeat ablation, adding a device, or exploring advanced options like hybrid ablation or left atrial appendage closure. Avoid ignoring subtle heart symptoms, and never adjust or stop medication without medical advice.
Best Practices for Living with Afib
Managing afib extends beyond medical treatment—it involves healthy lifestyle choices and proactive care. For women, being alert to subtler heart disease symptoms—such as fatigue, back or jaw pain, and disrupted sleep—can be crucial. Stay up to date with checkups, report any new symptoms to your healthcare provider, and seek assessment if there is a family history of heart conditions. Avoid smoking, limit alcohol, reduce sodium intake, and engage in regular moderate physical activity. Managing stress and other conditions, like high blood pressure, will further support your heart health. With the right approach and support, you can live well with afib and reduce the risk of complications